Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ACOS(number)
- number - The value to get the inverse cosine of. The number must be between -1 and 1 inclusive.
Using the ACOS function
The ACOS function returns the inverse cosine of a value. Input to the arc-cosine function must be between -1 and 1, inclusive. Geometrically, given the ratio of a triangle’s adjacent side over its hypotenuse, the function returns the angle of the triangle. For example, given a ratio of 0.5, the function returns an angle of 1.047 radians.
=ACOS(0.5) // Returns 1.047 radians
Convert Result to Degrees
To convert the result from radians to degrees, multiply the result by 180/PI() or use the DEGREES function. For example, to convert the result of ACOS(0.5) to degrees, you can use either formula below:
=ACOS(0.5)*180/PI() // Returns 60 degrees
=DEGREES(ACOS(0.5)) // Returns 60 degrees
Explanation
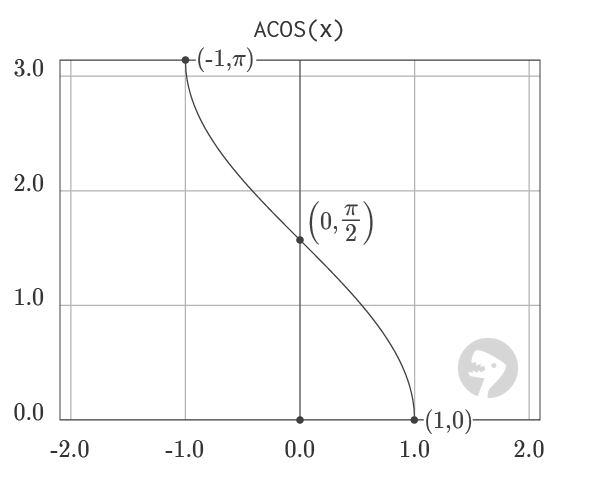
The graph of ACOS visualizes the output of the function in the range from -1 to 1. ACOS is the inverse of the COS function. However, because COS is a periodic function, the output of ACOS is limited to the range from 0 to π.
Graph courtesy of wumbo.net .
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ACOSH(number)
- number - The number to get the inverse hyperbolic cosine of.
Using the ACOSH function
The Excel ACOSH function returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number. Given the input 2.0, the function returns the value 1.316957897.
=ACOSH(2) // returns 1.316957897
Explanation
Given the x -component of a point that lies on the right branch of the unit hyperbola given by the equation x² - y² = 1, the ACOSH function returns the hyperbolic angle formed by the point.
=ACOSH(1.543080634) // returns 1
In other words, the ACOSH function returns twice the area of the sector formed between the origin, the x-axis, and the point on the hyperbola.

Notes
- The function throws a #NUM! Error when given a number less than 1.
Images courtesy of wumbo.net .