Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ATAN(number)
- number - The value to get the inverse tangent of.
Using the ATAN function
The Excel ATAN function returns the inverse tangent or arc-tangent of a number. In geometric terms, the function returns the angle of a right-triangle given the ratio of its opposite side over its adjacent side. The ATAN function is the inverse of the TAN function. For example, if the length of a right-triangle’s adjacent side is 3 and the length of its opposite side is 3 to find the angle of the triangle the formula is:
=ATAN(3/3) // Returns 0.785 radians
Convert Result to Degrees
ATAN returns the angle in radians. To convert the result from radians to degrees, multiply the result by 180/PI() or use the DEGREES function . For example, to convert the result of ATAN(1) to degrees, you can use either formula below:
=ATAN(1)*180/PI() // Returns 45 degrees
=DEGREES(ATAN(1)) // Returns 45 degrees
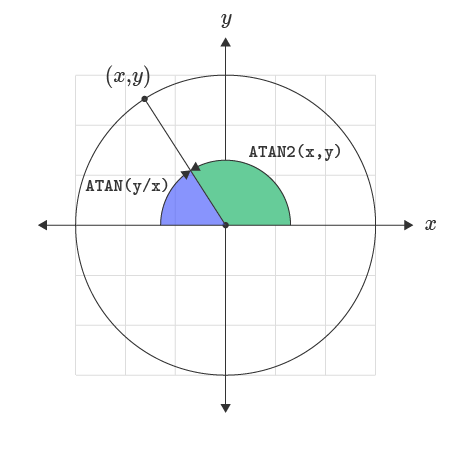
Difference Between ATAN and ATAN2
The ATAN2 function is useful for getting the angle corresponding to a point in the Cartesian Coordinate System which forms the shape of a right-triangle. For points in the first and fourth quadrants of the coordinate system, ATAN and ATAN2 will return the same angle as expressed in the formula:
=ATAN(y/x)=ATAN2(x,y)
For points in the second and third quadrants of the coordinate system, the ATAN function will return the angle relative to the negative x-axis direction. The ATAN2 function, by comparison, returns the angle relative to the positive x-axis which is the standard for measuring angles.

Graph
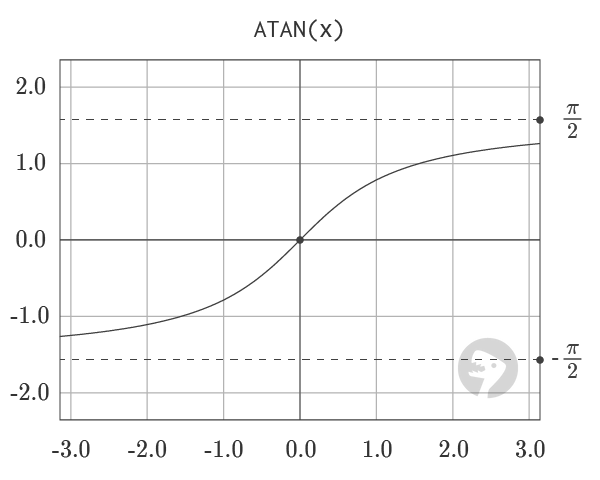
The graph of ATAN, shown above, visualizes the output of the function. Output of the function is limited to the range from -π/2 to π/2.
Images courtesy of wumbo.net .
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ATAN2(x_num,y_num)
- x_num - The x coordinate of the input point.
- y_num - The y coordinate of the input point.
Using the ATAN2 function
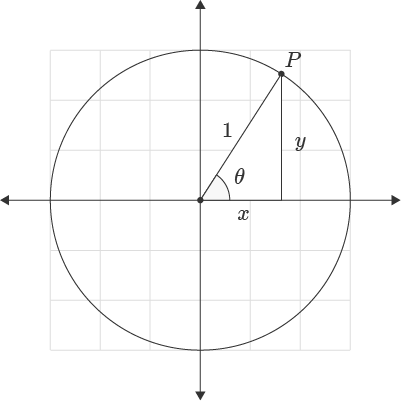
The Excel ATAN2 function returns the arctangent from the x and y coordinates of a point. In geometric terms, the function returns the radian angle corresponding to the coordinates of the input point. If you imagine a ray starting from the origin of the coordinate system and extending outwards, every point along the ray will return the same angle value. A circle of radius one demonstrates all possible return values for the function.
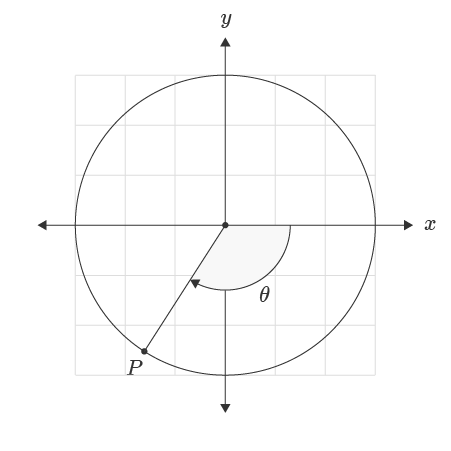
For negative y-values the function returns a negative angle. An angle is measured from the positive x-axis direction with the positive direction in the counter-clockwise direction and the negative direction in the clockwise direction.
Convert Output to Degrees
To convert the output of the ATAN2 function from radians to degrees the formula is:
=ATAN2(x,y)*180/PI() // Returns angle in degrees
Alternatively, the degrees formula can be used to convert the angle to degrees.
=DEGREES(ATAN2(x,y))// Returns angle in degrees
Difference Between ATAN and ATAN2
For points in the first and fourth quadrant, the ATAN2 function returns identical output to the ATAN function. This relationship is expressed in the formula below:
= ATAN2(x,y) = ATAN(y/x)
For points in the second and third quadrant, the ATAN function returns the angle relative to the negative x-direction axis.