Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=BITRSHIFT(number,shift_amount)
- number - The number to be bit shifted.
- shift_amount - The amount of bits to shift to the right, if negative shifts bits to the left instead.
Using the BITRSHIFT function
Integer underflow results in loss of the least significant bits. For example, if the number 3 is shifted right by one, then the right-most binary bit is truncated and lost. For any bit shift that results in integer overflow, where the result is larger than 2^48 -1, the function returns the #NUM! error.
How It Works
The shift_amount can either be positive or negative. If a negative number is provided, the bits are shifted to the left instead.
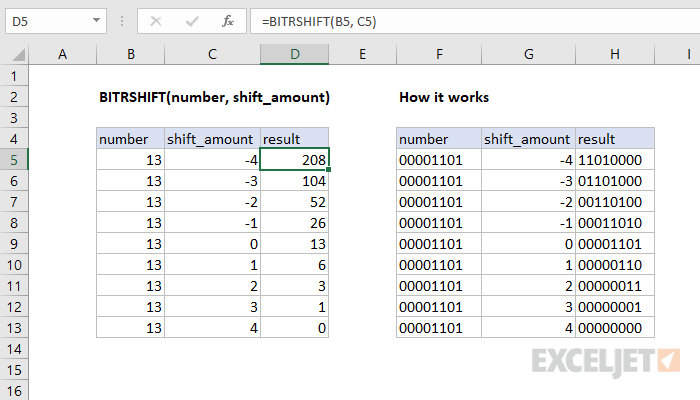
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=BITXOR(number1,number2)
- number1 - A positive decimal number.
- number2 - A positive decimal number.
Using the BITXOR function
The input numbers must be greater than or equal to zero and no larger than 2^48 - 1.
Difference Between OR and XOR
When a waiter in a breakfast diner asks if you want coffee OR orange juice, they are really asking if you want coffee XOR juice. You can have one or the other, but not both.