Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=HEX2DEC(number)
- number - The hexadecimal number you want to convert to decimal.
Using the HEX2DEC function
- The input number must be less than or equal to ten alpha-numeric characters, otherwise the function returns the #NUM! error value.
- The internal (binary) representation of the hexadecimal number uses two’s complement notation. The first bit indicates whether the number is positive or negative, and the other 39 bits indicate the magnitude of the number.
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
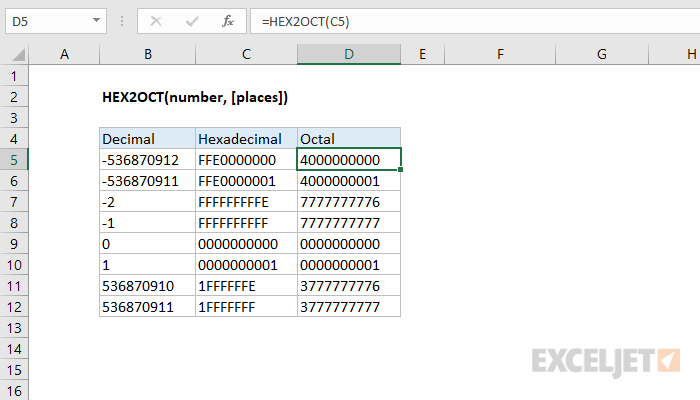
=HEX2OCT(number,[places])
- number - The hexadecimal number you want to convert to octal.
- places - [optional] Pads the resulting binary number with zeros up to the specified number of digits. If omitted returns the least number of characters required to represent the number.
Using the HEX2OCT function
- Excel only converts to octal numbers of 10-digits or less, restricting the range of valid input to [0, 7777777777] (octal).
- The input number must be less than or equal to ten alpha-numeric characters, otherwise the function returns the #NUM! error value.
Negative Numbers
Excel interprets both octal and hexadecimal numbers using two’s complement notation. Two’s complement notation is a convention that computers use to represent negative numbers in binary.