Explanation
In this example, the goal is to join different parts of a name (first, middle, last) into a full name. This is an example of concatenation . To concatenate means to join one text value to another with a formula, or in a more general programming language. In a current version of Excel, the simplest approach is to use the TEXTJOIN function, which is a flexible function for concatenating values in Excel. In an older version of Excel, you can use manual concatenation with the ampersand (&) operator, or you can use the older CONCATENATE function. The article below discusses all three approaches.
Note: Formulas that use concatenation in Excel are quite common, so it is a skill worth knowing. For a more detailed explanation of concatenation see How to concatenate in Excel .
TEXTJOIN solution
In the current version of Excel, the easiest way to join different parts of a name together is to use the TEXTJOIN function . To join the First name in column B to the Last name in column D together with TEXTJOIN the formula in cell F5 looks like this:
=TEXTJOIN(" ",1,B5,D5)
The inputs to TEXTJOIN are as follows:
- delimiter - a single space (" “)
- ignore_empty - 1, equivalent to TRUE
- text1 - B5, the first name
- text2 - D5, the last name
With this configuration, TEXTJOIN joins the first name in cell B5 to the last name in cell D5 together with a single space (” “) between them. If either value is empty, the ignore_empty argument set to 1 will cause TEXTJOIN to ignore the empty value and return the other value without a space.
You can easily adapt this formula to join all three names (first, middle, and last) together with TEXTJOIN. The formula used to perform this task in H5 looks like this:
=TEXTJOIN(" ",1,B5:D5)
- delimiter - a single space (” “)
- ignore_empty - 1, equivalent to TRUE
- text1 - the range B5:D5
Note that in this case, we give TEXTJOIN the range B5:D5 as text1 . TEXTJOIN will join all three values together separated by a single space (” “). Because ignore_empty is set to 1 (equivalent to TRUE in Excel), when a middle name is not present, TEXTJOIN will ignore that value and not add an extra space between the first and last names.
Note: newer versions of Excel also offer the CONCAT function (which replaces the CONCATENATE function in functionality). However, in this case, the TEXTJOIN function is a better option because it can automatically ignore empty values.
Manual concatenation solution
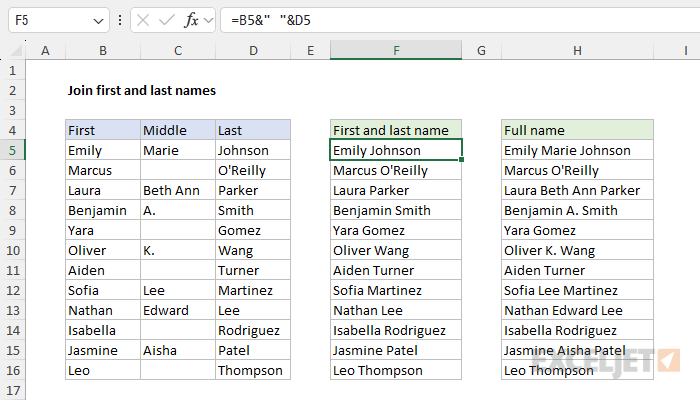
In an older version of Excel that does not offer the TEXTJOIN function, you can use manual concatenation with the ampersand (&) operator . This is often the technique used by more advanced users because it is simple and flexible. To join the first name in column B to the last name in column D together, you can use a formula like this:
=B5&" "&D5
The result is the first name in cell B5 joined to the last name in cell D5 separated by a space (” “). To use the manual concatenation to join the first, middle, and last names together, the formula in H5 is a bit more complex:
=B5&" "&IF(C5<>"",C5&" ","")&D5
At the core, this formula is similar to the first formula above. We begin with the first name in B5 and end with the last name in cell D5. However, to avoid adding an extra space when the middle name is blank we use the IF function to apply some conditional logic like this:
IF(C5<>"",C5&" ","")
The translation for this formula is: If cell C5 is not empty, return the value in C5 joined to a single space. If C5 is empty, return an empty string (”"). In other words, if there is a middle name, add it with a space, otherwise, add nothing.
Note: When you use concatenation in a formula, be sure to enclose any literal text in double quotes (""). However, do not enclose the ampersand (&) or cell references in quotes .
CONCATENATE solution
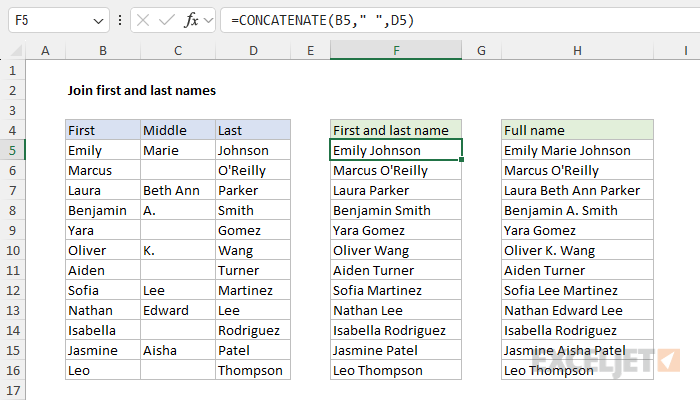
Another way to solve this problem is with the older CONCATENATE function . In the worksheet below the formula in cell F5 is:
=CONCATENATE(B5," ",D5)
And the formula in H5 looks like this:
=CONCATENATE(B5," ",IF(C5<>"",C5&" ",""),D5)
In the formula above, we aren’t able to avoid using the ampersand (&) entirely, because we still need the conditional logic created by the IF function to avoid adding extra space when the middle name is not present. This is something that TEXTJOIN handles automatically, which makes it a better option in more current versions of Excel.
Explanation
The goal in this example is to reformat names that appear in mixed upper and lower case letters into “proper case”, defined as each word in the name beginning with a capital letter. This can easily be done in Excel with the PROPER function.
PROPER function
The PROPER function automatically reformats text so that all words are capitalized. At the same time, it lowercases all other text. For example:
=PROPER("ben franklin") // returns "Ben Franklin"
=PROPER("ben FRANKLIN") // returns "Ben Franklin"
In the example shown, the formula in cell D5 is:
=PROPER(B5)
As the formula is copied down, it returns the names in column B with each word capitalized. In cases where a name is all uppercase, it converts the name to lowercase, and then capitalizes each word.
Removing extra space
If names contain extra space characters, you can normalize spaces and convert to proper case in one step by nesting the TRIM function inside PROPER like this:
=PROPER(TRIM("ben franklin ")) // returns "Ben Franklin"
The TRIM function removes leading and trailing spaces and converts runs of spaces to a single space. The result is returned to PROPER, which capitalizes each word as before.
Last name first
It is also possible to restructure the name so that the last name appears first, followed by the first and middle name as seen in the workbook below. The formula in cell D5 is:
=PROPER(TEXTAFTER(B5," ",-1)&", "&TEXTBEFORE(B5," ",-1))
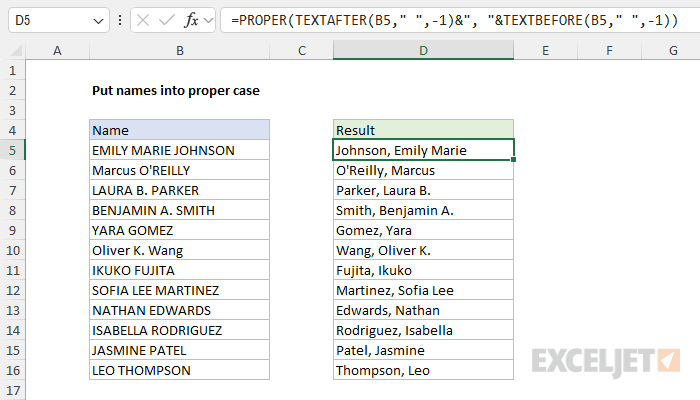
Working from the inside out, the TEXTAFTER function extracts the last name:
TEXTAFTER(B5," ",-1) // returns "JOHNSON"
The TEXTBEFORE function extracts the first and middle names:
TEXTBEFORE(B5," ",-1) // returns "EMILY MARIE"
Next, the two values are joined together with concatenation :
="JOHNSON"&", "&"EMILY MARIE"
="JOHNSON, EMILY MARIE"
Finally, the PROPER function capitalizes each name:
=PROPER("JOHNSON, EMILY MARIE")
="Johnson, Emily Marie"
Both TEXTBEFORE and TEXTAFTER have many options. For more information, see these links:
- Excel TEXTBEFORE function
- Excel TEXTAFTER function