Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=MINVERSE(array)
- array - A square array of numbers only.
Using the MINVERSE function
The MINVERSE function returns the inverse matrix of a given array. The product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix , a n × n square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros in every other position.
The MINVERSE function takes just one argument, array , which should be a square matrix, with an equal number of rows and columns. In order for MINVERSE to calculate an inverse matrix, array must contain numbers only. When an inverse exists, MINVERSE returns an inverse matrix with the same dimensions as the array provided.
If a matrix cannot be inverted, MINVERSE will return a #NUM! error. A matrix that can’t be inverted has a determinant of zero (0).
Examples
In the example shown the formula used in E7 to calculate the inverse matrix of the 2 x 2 matrix in the range B7:C8 is:
=MINVERSE(B7:C8) // returns {-2,3;3,-4}
The result is the 2 x 2 matrix seen in E7:F8, which can also be expressed as the array {-2,3;3,-4}.
The formula in M7 calculates the inverse matrix of the 3 x 3 matrix in B7:C8:
=MINVERSE(I7:K9) // returns {-24,20,-5;18,-15,4;5,-4,1}
The result is the 3 x 3 matrix seen in M7:O9, which can be expressed as the array {-24,20,-5;18,-15,4;5,-4,1}.
Array syntax
The MINVERSE function returns an array of values. In Excel 365 , where dynamic arrays are native , you can use the MINVERSE function without any special handling – MINVERSE will return an array of values that spill directly into cells in the worksheet.
In versions of Excel prior to Excel 365, you need to enter MINVERSE enter as a multi-cell array formula to display results directly on the worksheet. To do this, make a selection of the right size, and enter MINVERSE with control + shift + enter .
Notes
- The input array must be a square matrix with an equal number of rows and columns
- The array argument can be provided as a range or array constant like {4,3;3,2}
- Empty cells in the source array will cause MINVERSE to return the #VALUE! error
- MINVERSE returns the #VALUE! error value if array does not have an equal number of rows and columns.
- If a matrix cannot be inverted, MINVERSE will return a #NUM! error.
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=MMULT(array1,array2)
- array1 - The first array to multiply.
- array2 - The second array to multiply.
Using the MMULT function
The MMULT function returns the matrix product of two arrays, sometimes called the “dot product”. The result from MMULT is an array that contains the same number of rows as array1 and the same number of columns as array2 . The MMULT function appears in certain more advanced formulas that need to process multiple rows or columns. For example, you can use MMULT with XLOOKUP to match a value in any column .
The MMULT function takes two arguments , array1 and array2 , both of which are required. The column count of array1 must equal the row count of array2 . For example, you can multiply a 2 x 3 array by a 3 x 2 array to return a 2 x 2 array result. The MMULT function will return a #VALUE! error if array1 columns do not equal array2 rows.
Note: In Excel 365 , which supports dynamic arrays , MMULT spills multiple values on the worksheet. In earlier versions, you will need to enter as a multi-cell array formula with control + shift + enter.
Example #1 - basic usage
In the example shown, the MMULT formula is evaluated like this:
=MMULT(B6:D7,F6:G8)
=MMULT({0,3,5;5,5,2},{3,4;3,-2;4,-2})
={29,-16;38,6}
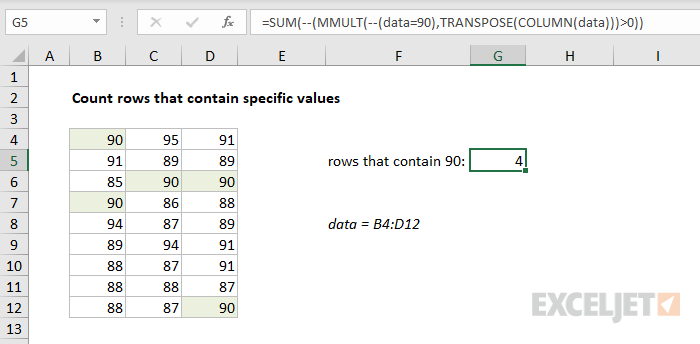
Example #2 - count rows with specific value
In this example, the goal is to count rows that contain the number 90. The challenge is that the value might appear in any of several columns, and might appear in more than one column of the same row. The MMULT function is used to condense results from multiple columns into a single 1-column array that can then be summed with the SUM function. The formula in G5 is:
=SUM(--(MMULT(--(data=90),TRANSPOSE(COLUMN(data)))>0))
Read a detailed explanation here . See below for more examples.
Notes
- Arrays must contain numbers only.
- Columns in array1 must equal the rows in array2 .
- Array1 and array2 can be provided as cell ranges, array constants, or references.
- MMULT returns #VALUE! if any cells in array1 and array2 are not numbers
- MMULT returns #VALUE! if array1 columns do not equal array2 rows.