Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=PERCENTRANK.INC(array,x,[significance])
- array - Array of data values.
- x - Value to rank.
- significance - [optional] Number of significant digits in result. Defaults to 3.
Using the PERCENTRANK.INC function
The Excel PERCENTRANK.INC returns the relative standing of a value within a data set as a percentage. For example, a test score greater than or equal to 80% of all test scores is said to be at the 80th percentile. In this case, PERCENTRANK.INC will assign a rank of .80 to the score. In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=PERCENTRANK.INC(data,B5)
where “data” is the named range C5:C12.
Note: The PERCENTRANK.INC function replaces PERCENTRANK , which is now classified as a " compatibility function “.
Interpolation
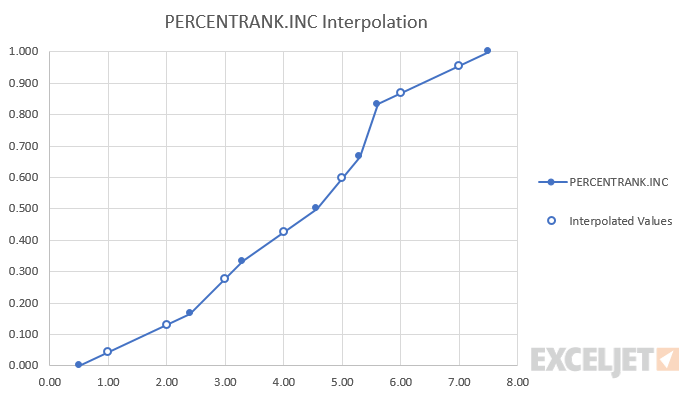
When x does not exist within the array, the function interpolates a value between data points. For example, when the x value of 4.00 is passed as an argument to the function, the percentage is interpolated to 42.4%, which lies between the percent ranks of 3.3 and 4.56, which are 33.3% and 50.0%, respectively.
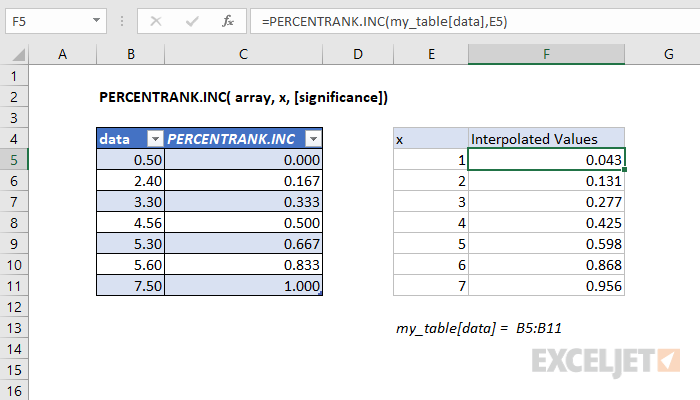
In the graph below, solid blue dots represent x values contained within the input array, while the outlined blue dots represent interpolated values.
Inclusive vs. Exclusive
Starting with Excel 2010, the PERCENTRANK function has been replaced by two distinct functions: PERCENTRANK.INC and PERCENTRANK.EXC . Both functions use the same arguments, but they differ in how they handle the boundaries of the dataset:
- PERCENTRANK.INC (Inclusive): Calculates the percentage rank of a value within the full range of the dataset, including the first and last values. The output is within the range [0,1], inclusive of the endpoints.
- PERCENTRANK.EXC (Exclusive): Calculates the percentage rank in a slightly different way by conceptually adding two virtual values—one smaller than the smallest actual value and one larger than the largest actual value. As a result, the percentage rank of the smallest value will be slightly above 0, and the rank of the largest value will be slightly below 1. The output falls within the range (0,1), exclusive of the endpoints.
The screen below shows differences with a small data set:


As the size of the input array increases, the difference between the two functions decreases. The difference between the returned percentages will never be larger than 1/(N+1), where N is the size of the input array.
Notes
- If x does not exist in the array, PERCENTRANK.INC interpolates to find the percentage rank.
- When significance is omitted PERCENTRANK.INC returns three significant digits (0.xxx)
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=PERMUT(number,number_chosen)
- number - The total number of items.
- number_chosen - The number of items in each combination.
Using the PERMUT function
The PERMUT function returns the number of permutations for a given number of items. A permutation is a combination where order matters. In other words, a permutation is an ordered combination.
There are two types of permutations:
- Permutations where repetition is not allowed (i.e. 123)
- Permutations where repetition is allowed (i.e. 333)
The PERMUT function calculates permutations where repetitions are not allowed. To calculate permutations where repetitions are allowed, use the PERMUTATIONA function .
Example
To use PERMUT, specify the total number of items and " number_chosen “, which represents the number of items in each combination. For example, to calculate 3-number permutations for the numbers 0-9, there are 10 numbers and 3 chosen, so the formula is:
=PERMUT(10,3) // returns 720
This result can be seen in cell D8 in the example shown.
Notes
- A permutation is a group of items in which order/sequence matters .
- If order is not significant, see the COMBIN function .
- Arguments that contain decimal values are truncated to integers.
- PERMUT returns a #VALUE! error value if either argument is not numeric.
- PERMUT returns #NUM! if number is less than number_chosen.