Pivot tables have a built-in feature to group dates by year, month, and quarter. In the example shown, a pivot table is used to summarize sales by year and quarter. Once the date field is grouped into years and quarters, the grouping fields can be dragged into separate areas, as seen in the example.
Fields
The source data contains two fields: Date, and Sales, and both are used create the pivot table, along with Years, which appears after dates are grouped:
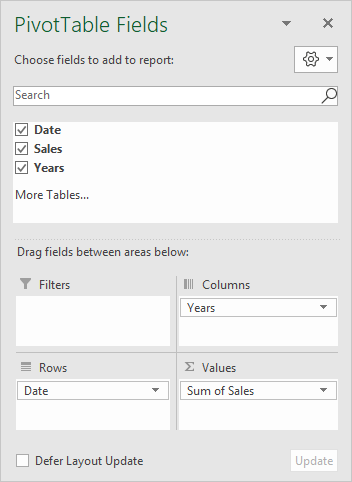
The Date field has been grouped by Years and Quarters:
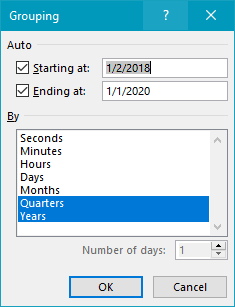
After grouping, the Years field appears in the field list, and the Date field displays quarters in the form “Qtr1”, “Qtr2”, etc. Years has been added as a Column field, and Date (Quarters) has been added as a Row field.
Finally, the Sales field has been added as a Value field, and set to Sum values:
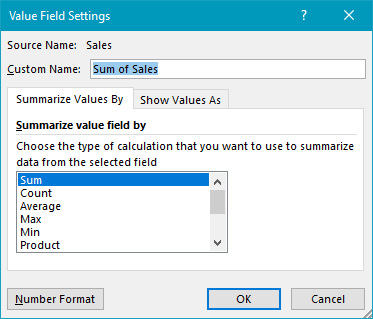
and the number format has been set to display currency.
Helper column alternative
As an alternative to automatic date grouping, you can add helper columns to the source data, and use a formula to extract the year , and another formula to create a value for Quarter . This allows you to assign custom abbreviations to quarters, and to calculate fiscal year quarters that don’t begin in January if needed. Once you have these values in helper columns, you can add them directly to the pivot table without grouping dates.
Steps
- Create a pivot table
- Add Date as a Column field, group by Years and Quarters
- Move Date (Quarters) to Rows area
- Add Sales field to Values area
- Change value field settings to use desired number format
Pivot tables have a feature to group dates by year, month, and quarter. In the example shown, a pivot table is used to summarize support issues by month and by priority. Each row in the pivot table lists the count of issues recorded in a given month by priority (A, B, C). The Total columns shows the total count of issues recorded in each month.
Note: the source data contains data for an entire year, but the pivot table is filtered to show only the first 6 months of the year, January through June.
Fields
The source data contains three fields: Issue , Date , and Priority . All three fields are used to create the pivot table:
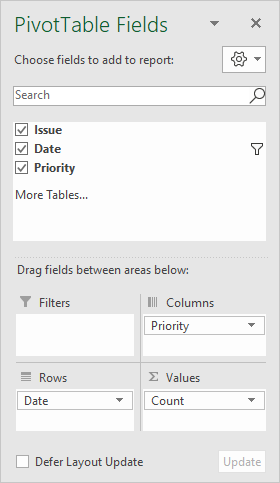
The Date field has been added as a Row field and grouped by month:
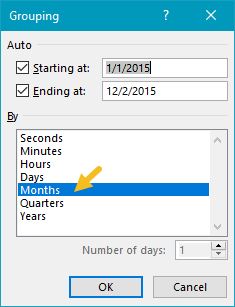
The Priority field has been added as a Column field.
The Issue field has been added as a Value field and renamed “Count” for clarity. Because Issue contains text field, the calculation is automatically set to Count:
<img loading=“lazy” src=“https://exceljet.net/sites/default/files/images/pivot/inline/pivot%20table%20issue%20count%20by%20priority%20value%20field%20settings.png" onerror=“this.onerror=null;this.src=‘https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEhe7F7TRXHtjiKvHb5vS7DmnxvpHiDyoYyYvm1nHB3Qp2_w3BnM6A2eq4v7FYxCC9bfZt3a9vIMtAYEKUiaDQbHMg-ViyGmRIj39MLp0bGFfgfYw1Dc9q_H-T0wiTm3l0Uq42dETrN9eC8aGJ9_IORZsxST1AcLR7np1koOfcc7tnHa4S8Mwz_xD9d0=s16000';" alt=“Value field settings - Issue renamed to “Count” - 6”>
COUNTIFS alternative
As an alternative to a pivot table, you can use the COUNTIFS function to count by month, as seen in this example .
Steps
- Create a pivot table
- Add Date field to Rows area, group by Month
- Add Priority field to Columns area
- Add Issue field Values area, rename to “Count”
Notes
- Any non-blank field in the data can be used in the Values area to get a count.
- When a text field is added as a Value field, Excel will display a count automatically.
- Without a Row field, the count represents all data records.