This is an example of a 100% stacked area chart. This tricky chart type can be quite hard to read. The idea is to visually show a percentage distribution across categories at specific intervals, but you lose the ability to compare absolute numbers, unless you add as data labels. In this case, data labels are only used to display the series name.
So, what can you see with this chart? Primarily, you can see that sales of Retrobags are collapsing while Organic Flannel makes up the slack. Hammocks and Banjo Packs are relatively stable. But what you can’t see is if overall sales are increasing (they are) or decreasing.
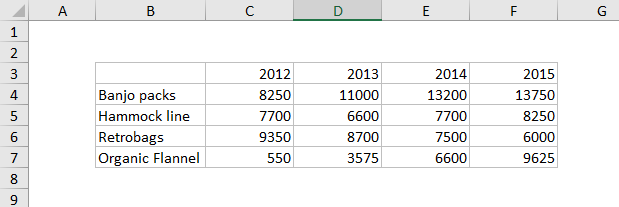
The data used to plot this chart looks like this:
How to create this chart
- Select the data and select line chart on the ribbon:
- Select the 100% Stacked Area option under 2d area
- Chart as inserted
- Select and delete legend
- Add data labels to chart:
- Select each data series. Check Series Name, then uncheck Value:
- Final 100% Stacked Area chart before title and size changes:
I was looking at an article on forbes.com about popular college degrees for women and men. They listed 9 degrees for both women and men (on many, many pages), and this chart is just a mash-up of the data they cited, sorted to show popular degrees for women at the top.
The chart type is 100% stacked bar, and its a good example of how a bar charts can accommodate extremely long labels. The data used in the chart looks like this:

How to make this chart
- Select data and insert column chart via ribbon:
- Choose 100% stacked bar chart under 2d bars:
- Chart as inserted:
- Select data series and increase bar width:
- Select each data series and set desired color.
- Select data series for women and reverse category:
- Add Data Labels:
- Move legend to top:
- Select and delete gridlines
- Set title as desired
- Final chart before resizing and adjusting font size: