Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=RANDBETWEEN(bottom,top)
- bottom - An integer representing the lower value of the range.
- top - An integer representing the upper value of the range.
Using the RANDBETWEEN function
The RANDBETWEEN function returns a random integer between two numbers. The result from RANDBETWEEN is automatic, and a new random number will be recalculated each time a worksheet is opened or changed.
RANDBETWEEN is a volatile function , and can cause performance issues in large or complex worksheets.
The RANDBETWEEN function takes two arguments : bottom and top . Bottom represents the lower bound for a random number, and top represents the upper bound. RANDBETWEEN includes both top and bottom values in the range of integers that may be returned.
Examples
Below are basic examples of RANDBETWEEN formulas:
=RANDBETWEEN(1,9) // random number between 1 and 9
=RANDBETWEEN(10,100) // random number between 10 and 100
=RANDBETWEEN(-10,0) // random number between -10 and zero
Multiple results
To generate multiple random numbers in multiple cells, select the target cells, enter the RANDBETWEEN function, and press control + enter to enter the same formula in all cells at once.
Static results
RANDBETWEEN returns a new random value each time the worksheet is recalculated, including changes made to unrelated cells in the same workbook. To stop random numbers from changing, copy the cells that contain RANDBETWEEN to the clipboard, then use Paste Special > Values to convert to text. To get a single random number that doesn’t change, enter RANDBETWEEN in the formula bar , press F9 to convert the formula to a static result, and press Enter to enter the value in the cell.
Note: in Excel 365 , the RANDARRAY function is a more flexible alternative. RANDARRAY can generate random decimal numbers and random integers, and can also return more than one random value at the same time.
Notes
- RANDBETWEEN recalculates whenever a worksheet is opened or changed.
- RANDBETWEEN returns integers. Use the RAND function to return random decimal values.
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ROMAN(number,[form])
- number - Number (in Arabic numeral) you want to convert to Roman numeral.
- form - [optional] The type of Roman numeral you want.
Using the ROMAN function
The ROMAN function converts a number to a Roman numeral. For example:
=ROMAN(4) // returns "IV"
=ROMAN(9) // returns "IX"
=ROMAN(99) // returns "XCIX"
=ROMAN(100) // returns "C"
ROMAN takes two arguments : number and form . Number should be a whole number between 1 and 3999. The form argument controls the convention used for Roman numbers. The argument is optional and the default is zero (0), which results in classic non-abbreviated Roman numbers. Other possible values are 1-4, which specify progressively more concise output. For example:
=ROMAN(1999,0) // returns "MCMXCIX"
=ROMAN(1999,2) // returns "MXMIX"
=ROMAN(1999,4) // returns "MIM"
See more form samples below .
Roman numbers
The table below lists available Roman numbers with their equivalent Arabic number value.
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| V | 5 |
| X | 10 |
| L | 50 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 500 |
| M | 1000 |
The ROMAN function converts Arabic numbers to Roman numbers. Use the ARABIC function to convert Roman numbers to Arabic numbers.
Abbreviated syntax
The ROMAN function can output Roman numbers in a more abbreviated syntax, controlled with the form argument. The screen below shows how different values for form affect output.
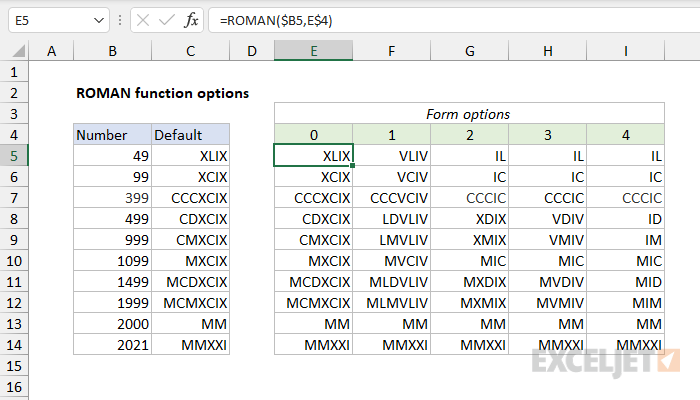
Notes
- Number should be a positive number between 1 and 3999.
- Number should be a whole number; decimal values are ignored.
- If number is negative or out of range, ROMAN returns #VALUE!
- The ROMAN function performs the opposite conversion as the ARABIC function .
- The form argument controls Roman numeral abbreviation. Valid inputs are 0-4.