Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=TEXTJOIN(delimiter,ignore_empty,text1,[text2],...)
- delimiter - Separator between each text.
- ignore_empty - Whether to ignore empty cells or not.
- text1 - First text value or range.
- text2 - [optional] Second text value or range.
Using the TEXTJOIN function
The TEXTJOIN function concatenates multiple values together with or without a delimiter. TEXTJOIN can concatenate values provided as cell references, ranges, or constants, and can optionally ignore empty cells.
The TEXTJOIN function takes three required arguments : delimiter , ignore_empty , and text1 . Delimiter is the text to use between values that are concatenated together and should be enclosed in double-quotes (""), for example, a space (" “) or a comma with a space (”, “). To use no delimiter, supply an empty string (”"). Ignore_empty is a Boolean (TRUE/FALSE) value that controls whether empty values should be ignored or added to the result. This is often set to TRUE to avoid delimiters with no content in the result from TEXTJOIN. Text1 is the first value to join together. This can be a cell reference, a range, or a hard-coded text value. Subsequent optional arguments, text2 , text3 , text4 , etc. can be provided up to 252 values total.
Values are concatenated in the order they appear. With “Hello” in A1 and “World” in A2, the following formula returns “Hello World”:
=TEXTJOIN(" ",TRUE,A1,A2) // returns "Hello World"
Changing the delimiter to a comma (", “) and reversing A1 and A2, we get “World, Hello”:
=TEXTJOIN(", ",TRUE,A2,A1) // returns "World, Hello"
Concatenating a range
To join cells in the range A1:A3 with a comma and space, you can use TEXTJOIN like this:
=TEXTJOIN(", ",TRUE,A1:A3)
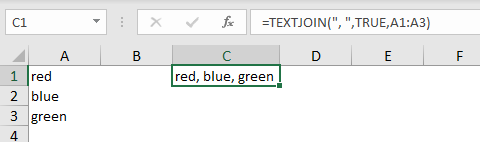
The second argument, ignore_empty, controls behavior for empty cells and text values. If set TRUE, empty values are skipped so that the delimiter is not repeated in the final result. If set to FALSE, TEXTJOIN will include empty values in the output.
Name with title
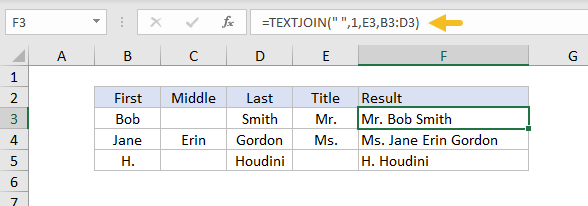
In the example below, TEXTJOIN is set up to concatenate names. Notice the cell reference for Title is provided first, followed by a range for First, Middle, and Last. Ignore empty is set to 1 (TRUE) to avoid adding extra space to names without Middle or Title values. The formula in F3 is:
=TEXTJOIN(" ",1,E3,B3:D3)
Number formatting
When concatenating numbers, number formatting is lost. For example, with the date 1-Jul-2021 in cell A1, and 2-Jul-2021 in A2, the dates revert to serial numbers :
=TEXTJOIN("-",1,A1,A2) // returns "44378-44379"
Use the TEXT function to apply formatting during concatenation:
=TEXTJOIN("-",1,TEXT(A1,"mmm d"),TEXT(A2,"mmm d")) // "Jul 1-Jul 2"
The formula above returns the text “Jul 1-Jul 2”. Adjust the number formatting as desired.
TEXTJOIN versus CONCAT
TEXTJOIN and CONCAT are both newer functions in Excel that replace the older CONCATENATE function. Like the CONCAT function, TEXTJOIN will accept a range of cells to concatenate. The main difference is that TEXTJOIN also accepts a delimiter to use when joining values together.
Notes
- To concatenate manually, use the concatenation operator (&)
- The CONCAT function also provides basic concatenation, but provides no options for delimiters or empty values.
- Numbers provided to TEXTJOIN will be converted to text values during concatenation.
- TEXTJOIN is a new function, available in Office 365 and Excel 2019.
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=TRIM(text)
- text - The text from which to remove extra space.
Using the TRIM function
The TRIM function strips extra spaces from text, leaving only a single space between words, and removing any leading or trailing space. For example:
=TRIM(" A stitch in time. ") // returns "A stitch in time."
The TRIM function can be used together with the CLEAN function to remove extra space and strip out other non-printing characters:
=TRIM(CLEAN(A1)) // trim and clean
TRIM often appears in other more advanced text formulas. For example, the formula below will count the number of words in cell A1:
LEN(TRIM(A1))-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",""))+1
Because this formula depends on single spaces to get an accurate word count, TRIM is used to normalize space before the count is calculated. Full description here .
Notes
- TRIM strips extra spaces from text, leaving only single spaces between words and no space characters at the start or end of the text.
- TRIM is useful when cleaning up text that has come from other applications or environments.
- TRIM only removes the ASCII space character (32) from text.
- Unicode text often contains a non-breaking space character (160) that appears in web pages as an HTML entity. This will not be removed with TRIM.
- The CLEAN function strips the first 32 non-printing characters (ASCII values 0 through 31) from text.